Introduction
‘Everything everywhere all at once’ could very well sum up the times we live in, as shock upon shock continues to disrupt economies around the world. From the climate emergency to the ongoing wars, the closing down of several prominent banking operations, to massive global trade conflicts, risks are hitting us harder and faster than ever.
Meanwhile, new regulations continue to emerge, some of which aren’t in sync. Consumer behaviors keep changing. And with greater digitalization comes greater threats – cybercrime, deep fakes, tech failures, AI ethical issues, etc. Add to that supply chain disruptions and surging inflation, and it’s clear that we need new strategies to deal with risk.
Now more than ever, boards and leadership teams need to understand how risks interconnect with and influence each other. Decision-makers need real-time risk intelligence to anticipate and tackle those “unknown unknowns” while also capitalizing on growth opportunities.
None of these objectives can be achieved if governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) activities are managed in silos. It’s time to embrace a connected approach to GRC – one that can help you join the dots across all your data, processes, and systems to generate a complete, connected view of risk.
With better risk visibility, you can spot emerging risks ahead of time and know how and where they will impact your enterprise. You’ll also be able to uncover and act on opportunities faster because all the insights you need are at your fingertips. That’s the power of connected GRC. And that’s where the future lies.
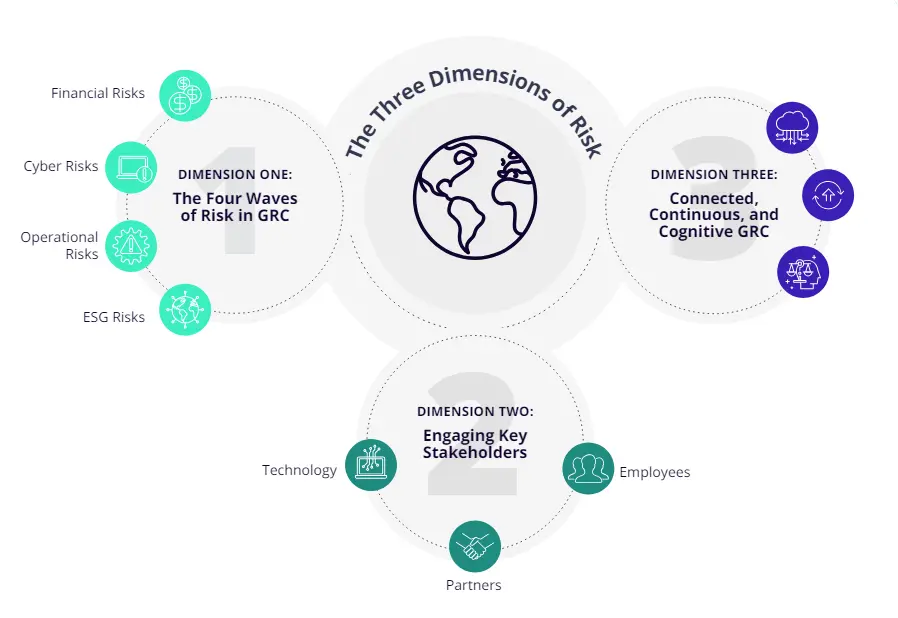
The Three Dimensions of Risk
Running a business in a volatile and complex environment can sometimes feel like an endless obstacle race. No sooner do you finish putting out one fire than two others appear. Many of the executives and risk professionals we talk to struggle with the question, “How can we make our organizations more agile and resilient?”
The answer, we’ve found, lies in three steps: understanding the various dimensions of risks that are hitting your organization, engaging and empowering your stakeholders to get ahead of the risks: and finally, simplifying risk management and monitoring through a connected, continuous, and cognitive approach to GRC.
This eBook will further explore the three dimensions of risk and how organizations can successfully navigate the expanding risk universe with an agile and innovative mindset.
Dimension One: The Four Waves of GRC
Over the past decade and a half, the world has grappled with multiple waves of risks. Each prompted organizations to reexamine and strengthen their GRC processes.
Here are the four most serious risks that every organization faces today:
Wave 1: Financial Risks
The Great Recession of 2008 was a shocking and eye-opening risk event for many organizations. We quickly learned that an interconnected world can create more extreme risks – both financial and non-financial. The Great Recession had a domino effect. When one part of the financial system toppled, it quickly pushed over other pieces. That’s why seemingly impervious financial giants like Bear Stearns and Lehman Brothers were instantly obliterated. Today, we’re seeing a similar domino effect with the COVID-19 aftershocks and the ongoing armed conflicts in several parts of the globe pushing up energy prices, triggering a cost-of-living crisis, and slowing down economic growth. Protecting against these kinds of global macroeconomic risks is now essential for every organization.
Wave 2: Cyber Risks
The 2010s saw an explosion of cyberattacks catalyzed by the meteoric rise in mobile phone and social media usage. Since then, cyber threats have only grown more sophisticated, pervasive, and costly. According to PwC, the percentage of organizations reporting costs of $1 million or more for their worst breach in the past three years rose to 36% from 27% last year. What’s evident through all this is that data is the new oil — it’s what powers the digital economy. And it’s the responsibility of every organization to ensure that the right data privacy and security controls are in place.
Wave 3: Operational Risks
From internal process failures to asset misappropriation and technological disruptions, operational risk incidents can cause substantial losses. Now, with organizations adopting ML/AI, cloud services, and cryptocurrencies, there are new risks to contend with – be it around data ethics, regulatory compliance, or third parties. The focus is increasingly on operational resilience, especially with the emergence of newer compliance requirements such as the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), the Bank of England’s Operational Resilience guidelines, and the upcoming Australian Prudential Regulation Authority’s (APRA’s) Prudential Standard CPS 230 for Operational Risk Management. Strong operational risk management programs, supported by data and analytics, will be key in balancing risk-reward outcomes, and adapting quickly to disruptions.
At the turn of the 2020s, the lives and livelihoods of people around the world were fundamentally disrupted by COVID-19. The virus, which spread like wildfire, didn’t just devastate public health systems – it also shut down businesses, triggered supply shortages, disrupted transport networks, and devastated industries. Almost overnight, businesses were forced to work remotely. Assumptions about workplace health, safety, and well-being were uprooted. Today, the worst of the pandemic appears to be behind us. But we cannot afford to be complacent. The future is likely to bring more frequent public health crises due to global warming, water shortages, antimicrobial resistance, and more such threats. Businesses must be prepared for all the resulting implications.
Wave 4: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Risks
The next wave bearing down on us could be the most serious of them all: ESG risks. Our world has been increasingly besieged by climate change issues such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and drought, as well as human health issues such as the COVID-19 pandemic. These events have taken an economic toll on businesses around the world. While many companies are committed to minimizing their carbon footprint and emissions, Accenture finds that only 18% of companies are on track to reach net zero in operations by 2050. The future is also likely to bring more frequent public health crises due to global warming, water shortages, antimicrobial resistance, and more such threats. Organizations must factor in ESG risks to stay agile and resilient.
Dimension Two: Serving Key Stakeholders
Everyone in the organization has a part to play in risk management – from the employees in the frontline, to the third parties in the extended ecosystem. When all these stakeholders are empowered to detect and manage risks well, they can make more risk-aware decisions that unlock new growth opportunities.
Employees
As the first key stakeholder group, employees must be intimately involved with the organization’s GRC initiatives. Pharmaceutical giant, Novartis, for example, crowdsourced its code of ethics based on shared ideas and insights from thousands of global employees. Novartis called it the “unbossing” of their code of ethics because the effort wasn’t driven top-down but bottom-up.
Partners
Third-party partners such as vendors, suppliers, and customers are the next key stakeholder group. From within this group originate many of today’s biggest risks – be it data breaches, emissions, or software failures. As companies outsource more of their operations and data processing activities, it’s imperative to have a strong third-party risk management program in place. Proper due diligence, screening, and risk assessments can help you get the most value out of your third-party relationships while minimizing the associated risks.
Technology
The next emerging GRC stakeholders are AI and bots, along with humans. Many companies now have thousands of bots and virtual agents to help them run their operations. These agents are increasingly present on the frontlines to engage customers, provide personalized recommendations, and resolve service queries. But bots could also be the door through which cyber criminals gain access to sensitive customer information or launch phishing attacks. In fact, the next big risk event could be caused by a bot malfunction, whether due to malicious design or an accident. AI cannot be left alone as an ungoverned activity.
Dimension Three: Connected, Continuous, And Cognitive GRC
An agile organization is built on the foundations of connected GRC strategy with continuous risk and control monitoring and cognitive technologies.
Connected GRC is about understanding how various risks intertwine and amplify each other’s impact. For example, a cybersecurity risk such as a breach at a chemical facility could result in ESG risks such as hazardous waste being leaked into surrounding ecosystems. Understanding these interdependencies is essential in building organizational resilience. It starts by replacing siloed GRC processes with a connected GRC approach. Here, risks are mapped to controls, testing processes, assets, and objectives for a complete view of the risk universe. What’s more, risk, compliance, audit, cyber, and ESG functions can collaborate and share risk information seamlessly.
Continuous GRC is about reducing business losses and increasing operating effectiveness through automated risk and control monitoring. In this approach, it isn’t just a sample of risks and controls that are tested at periodic intervals but full populations that are monitored frequently and cost-effectively. Automated, continuous testing ensures that risks are in check and that controls are working as intended. It also strengthens compliance, reduces risk management efforts, and helps rationalize controls.
Cognitive GRC represents a paradigm shift in GRC-powered decision-making within organizations. With GRC processes now leveraging cognitive technologies, including AI, automation, natural language processing, machine learning, LLM, generative AI, and predictive modeling, to process vast amounts of GRC information, GRC practitioners are now enabled to work smarter by automating tasks and connecting the dots across their risk universe. Through real-time risk responses and immediate flagging of compliance issues, GRC professionals can make informed decisions swiftly. Moreover, these technologies provide high-quality metrics, offering near real-time insights into the performance of risk management, ESG, cybersecurity, and other GRC initiatives. This, in turn, aids stakeholders in prioritizing investments and allocating resources more effectively as well.
Tone from the Top
Effective GRC starts at the top, with the C-suite and board. They’re the ones who establish the organization’s culture, risk frameworks, and ethical climate. When they demonstrate the importance of risk management, compliance, sustainability, and social responsibility through both their words and actions, the rest of the enterprise will fall in line.
The leadership team is also responsible for overseeing GRC – ensuring that risks are well within their thresholds, compliance is on track, cyber threats are in check, environmental policies and procedures are being followed, etc. This kind of oversight is best achieved with a single source of GRC truth that can consolidate risk, compliance, cyber, and sustainability data from across the enterprise into a unified view. With this data, executives and boards can make more informed decisions in less time.
The most successful leaders see GRC as a competitive advantage rather than a checklist item. They know that GRC done well will not only help them meet their compliance obligations, but also inspire trust with customers, investors, and stakeholders.
The Three Dimensions of Risk
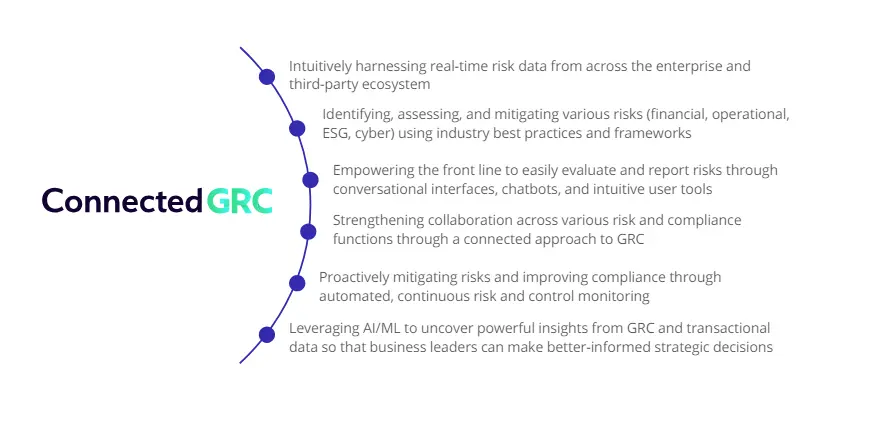
MetricStream ConnectedGRC
MetricStream’s ConnectedGRC empowers organizations to strengthen agility and resilience through faster, better visibility into risks. The platform integrates risk management, compliance, audit, cybersecurity, and sustainability activities in a single source of truth – so, organizations can seamlessly coordinate GRC activities while also getting all the insights needed to mitigate risks. Designed with advanced analytics and AI capabilities at its core, MetricStream’s ConnectedGRC delivers GRC best practices to meet the evolving needs of today’s dynamic enterprises.
Stay future-ready by:
What’s Next
With a robust GRC program and platform, risk management no longer remains a brake on the business. Rather, it becomes an accelerator that enables you to smoothly navigate turns and obstacles at high speed while remaining firmly on the road to success.
‘Everything everywhere all at once’ could very well sum up the times we live in, as shock upon shock continues to disrupt economies around the world. From the climate emergency to the ongoing wars, the closing down of several prominent banking operations, to massive global trade conflicts, risks are hitting us harder and faster than ever.
Meanwhile, new regulations continue to emerge, some of which aren’t in sync. Consumer behaviors keep changing. And with greater digitalization comes greater threats – cybercrime, deep fakes, tech failures, AI ethical issues, etc. Add to that supply chain disruptions and surging inflation, and it’s clear that we need new strategies to deal with risk.
Now more than ever, boards and leadership teams need to understand how risks interconnect with and influence each other. Decision-makers need real-time risk intelligence to anticipate and tackle those “unknown unknowns” while also capitalizing on growth opportunities.
None of these objectives can be achieved if governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) activities are managed in silos. It’s time to embrace a connected approach to GRC – one that can help you join the dots across all your data, processes, and systems to generate a complete, connected view of risk.
With better risk visibility, you can spot emerging risks ahead of time and know how and where they will impact your enterprise. You’ll also be able to uncover and act on opportunities faster because all the insights you need are at your fingertips. That’s the power of connected GRC. And that’s where the future lies.
Running a business in a volatile and complex environment can sometimes feel like an endless obstacle race. No sooner do you finish putting out one fire than two others appear. Many of the executives and risk professionals we talk to struggle with the question, “How can we make our organizations more agile and resilient?”
The answer, we’ve found, lies in three steps: understanding the various dimensions of risks that are hitting your organization, engaging and empowering your stakeholders to get ahead of the risks: and finally, simplifying risk management and monitoring through a connected, continuous, and cognitive approach to GRC.
This eBook will further explore the three dimensions of risk and how organizations can successfully navigate the expanding risk universe with an agile and innovative mindset.
Over the past decade and a half, the world has grappled with multiple waves of risks. Each prompted organizations to reexamine and strengthen their GRC processes.
Here are the four most serious risks that every organization faces today:
Wave 1: Financial Risks
The Great Recession of 2008 was a shocking and eye-opening risk event for many organizations. We quickly learned that an interconnected world can create more extreme risks – both financial and non-financial. The Great Recession had a domino effect. When one part of the financial system toppled, it quickly pushed over other pieces. That’s why seemingly impervious financial giants like Bear Stearns and Lehman Brothers were instantly obliterated. Today, we’re seeing a similar domino effect with the COVID-19 aftershocks and the ongoing armed conflicts in several parts of the globe pushing up energy prices, triggering a cost-of-living crisis, and slowing down economic growth. Protecting against these kinds of global macroeconomic risks is now essential for every organization.
Wave 2: Cyber Risks
The 2010s saw an explosion of cyberattacks catalyzed by the meteoric rise in mobile phone and social media usage. Since then, cyber threats have only grown more sophisticated, pervasive, and costly. According to PwC, the percentage of organizations reporting costs of $1 million or more for their worst breach in the past three years rose to 36% from 27% last year. What’s evident through all this is that data is the new oil — it’s what powers the digital economy. And it’s the responsibility of every organization to ensure that the right data privacy and security controls are in place.
Wave 3: Operational Risks
From internal process failures to asset misappropriation and technological disruptions, operational risk incidents can cause substantial losses. Now, with organizations adopting ML/AI, cloud services, and cryptocurrencies, there are new risks to contend with – be it around data ethics, regulatory compliance, or third parties. The focus is increasingly on operational resilience, especially with the emergence of newer compliance requirements such as the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), the Bank of England’s Operational Resilience guidelines, and the upcoming Australian Prudential Regulation Authority’s (APRA’s) Prudential Standard CPS 230 for Operational Risk Management. Strong operational risk management programs, supported by data and analytics, will be key in balancing risk-reward outcomes, and adapting quickly to disruptions.
At the turn of the 2020s, the lives and livelihoods of people around the world were fundamentally disrupted by COVID-19. The virus, which spread like wildfire, didn’t just devastate public health systems – it also shut down businesses, triggered supply shortages, disrupted transport networks, and devastated industries. Almost overnight, businesses were forced to work remotely. Assumptions about workplace health, safety, and well-being were uprooted. Today, the worst of the pandemic appears to be behind us. But we cannot afford to be complacent. The future is likely to bring more frequent public health crises due to global warming, water shortages, antimicrobial resistance, and more such threats. Businesses must be prepared for all the resulting implications.
Wave 4: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Risks
The next wave bearing down on us could be the most serious of them all: ESG risks. Our world has been increasingly besieged by climate change issues such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and drought, as well as human health issues such as the COVID-19 pandemic. These events have taken an economic toll on businesses around the world. While many companies are committed to minimizing their carbon footprint and emissions, Accenture finds that only 18% of companies are on track to reach net zero in operations by 2050. The future is also likely to bring more frequent public health crises due to global warming, water shortages, antimicrobial resistance, and more such threats. Organizations must factor in ESG risks to stay agile and resilient.
Everyone in the organization has a part to play in risk management – from the employees in the frontline, to the third parties in the extended ecosystem. When all these stakeholders are empowered to detect and manage risks well, they can make more risk-aware decisions that unlock new growth opportunities.
Employees
As the first key stakeholder group, employees must be intimately involved with the organization’s GRC initiatives. Pharmaceutical giant, Novartis, for example, crowdsourced its code of ethics based on shared ideas and insights from thousands of global employees. Novartis called it the “unbossing” of their code of ethics because the effort wasn’t driven top-down but bottom-up.
Partners
Third-party partners such as vendors, suppliers, and customers are the next key stakeholder group. From within this group originate many of today’s biggest risks – be it data breaches, emissions, or software failures. As companies outsource more of their operations and data processing activities, it’s imperative to have a strong third-party risk management program in place. Proper due diligence, screening, and risk assessments can help you get the most value out of your third-party relationships while minimizing the associated risks.
Technology
The next emerging GRC stakeholders are AI and bots, along with humans. Many companies now have thousands of bots and virtual agents to help them run their operations. These agents are increasingly present on the frontlines to engage customers, provide personalized recommendations, and resolve service queries. But bots could also be the door through which cyber criminals gain access to sensitive customer information or launch phishing attacks. In fact, the next big risk event could be caused by a bot malfunction, whether due to malicious design or an accident. AI cannot be left alone as an ungoverned activity.
An agile organization is built on the foundations of connected GRC strategy with continuous risk and control monitoring and cognitive technologies.
Connected GRC is about understanding how various risks intertwine and amplify each other’s impact. For example, a cybersecurity risk such as a breach at a chemical facility could result in ESG risks such as hazardous waste being leaked into surrounding ecosystems. Understanding these interdependencies is essential in building organizational resilience. It starts by replacing siloed GRC processes with a connected GRC approach. Here, risks are mapped to controls, testing processes, assets, and objectives for a complete view of the risk universe. What’s more, risk, compliance, audit, cyber, and ESG functions can collaborate and share risk information seamlessly.
Continuous GRC is about reducing business losses and increasing operating effectiveness through automated risk and control monitoring. In this approach, it isn’t just a sample of risks and controls that are tested at periodic intervals but full populations that are monitored frequently and cost-effectively. Automated, continuous testing ensures that risks are in check and that controls are working as intended. It also strengthens compliance, reduces risk management efforts, and helps rationalize controls.
Cognitive GRC represents a paradigm shift in GRC-powered decision-making within organizations. With GRC processes now leveraging cognitive technologies, including AI, automation, natural language processing, machine learning, LLM, generative AI, and predictive modeling, to process vast amounts of GRC information, GRC practitioners are now enabled to work smarter by automating tasks and connecting the dots across their risk universe. Through real-time risk responses and immediate flagging of compliance issues, GRC professionals can make informed decisions swiftly. Moreover, these technologies provide high-quality metrics, offering near real-time insights into the performance of risk management, ESG, cybersecurity, and other GRC initiatives. This, in turn, aids stakeholders in prioritizing investments and allocating resources more effectively as well.
Effective GRC starts at the top, with the C-suite and board. They’re the ones who establish the organization’s culture, risk frameworks, and ethical climate. When they demonstrate the importance of risk management, compliance, sustainability, and social responsibility through both their words and actions, the rest of the enterprise will fall in line.
The leadership team is also responsible for overseeing GRC – ensuring that risks are well within their thresholds, compliance is on track, cyber threats are in check, environmental policies and procedures are being followed, etc. This kind of oversight is best achieved with a single source of GRC truth that can consolidate risk, compliance, cyber, and sustainability data from across the enterprise into a unified view. With this data, executives and boards can make more informed decisions in less time.
The most successful leaders see GRC as a competitive advantage rather than a checklist item. They know that GRC done well will not only help them meet their compliance obligations, but also inspire trust with customers, investors, and stakeholders.
MetricStream’s ConnectedGRC empowers organizations to strengthen agility and resilience through faster, better visibility into risks. The platform integrates risk management, compliance, audit, cybersecurity, and sustainability activities in a single source of truth – so, organizations can seamlessly coordinate GRC activities while also getting all the insights needed to mitigate risks. Designed with advanced analytics and AI capabilities at its core, MetricStream’s ConnectedGRC delivers GRC best practices to meet the evolving needs of today’s dynamic enterprises.
Stay future-ready by:

With a robust GRC program and platform, risk management no longer remains a brake on the business. Rather, it becomes an accelerator that enables you to smoothly navigate turns and obstacles at high speed while remaining firmly on the road to success.








