Introduction
Enterprise risk management is becoming an increasingly complex business function. Today, organizations must tackle multiple risks – cyber, geopolitical, third-party, physical, privacy, financial, ESG, and many more. With the larger business environment becoming increasingly digitized and interconnected with ongoing digital transformations, expansion of the internet, cloud adoption, and mobile computing, these diverse risk categories are constantly evolving and becoming more intertwined.
Organizations across industries need to develop a deeper understanding of all the risks they face and their interrelationships. The pandemic further underscored our interconnectedness. It has demonstrated that the volume and velocity of risks and intersection points would only increase going forward.
With the interconnectedness of risks continuing to intensify, organizations must adopt an integrated and holistic approach to risk management and the overarching governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) management framework. GRC professionals can no longer analyze risks in isolation – they need to understand their cascading impacts and devise business resilience strategies effectively.
This eBook will delve into the interconnectedness of risks, closely examine the intersection of third-party and cyber risks, and discuss key strategies for organizations to tackle complex risk relationships effectively.
Risk Interconnectivity – The Growing Web of Risk Relationships
Risks do not exist in isolation. There are always multiple points of intersection. Consider, for example, geopolitical risk. As a result of the continuous power conflicts among global powers, there will inevitably be supply chain disruptions, increased danger of state-sponsored cyber attacks, changes in government regulations and policies, and more. At the same time, cyber-attacks lead to operational, financial, reputational, and other risks, and so on. This interconnectedness of risks results in a complex web of risk relationships.
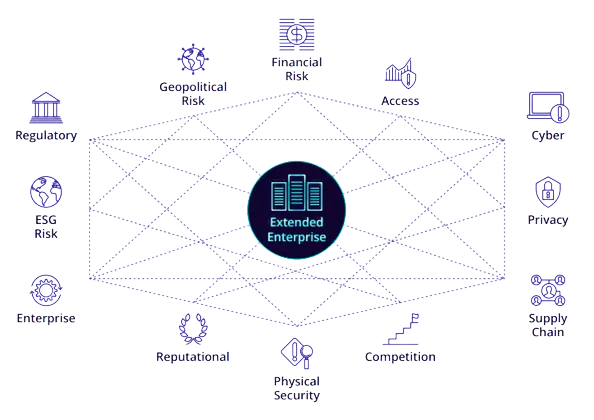
If these risks are not viewed from a macro-perspective, they will continue to evolve within their silos, eventually culminating in a systemic, industry-wide collapse.
Risk managers must assess the organizational risk posture by analyzing the impact of risk on all interrelated categories, including operational, strategic, systemic, regulatory, technology, security, third-party, and physical risks. A disruption anywhere along the transaction chain can cause ripples across the market. A failure to comprehend and assess interdependencies can lead to shortsighted decisions and hamper recovery efforts.
The traditional approach to risk management – relying on siloed processes, manual effort, and spreadsheets – falls short of providing comprehensive visibility into risks and risk relationships. A GRC strategy designed for the future must have an integrated and connected approach at its core. It should not only provide visibility into risk interconnectedness but also how risks are tied to assets, controls, regulations, processes, etc., for a true understanding of the overall GRC posture. Combined with automated and autonomous workflows, this forward-looking and resilience-focused GRC approach will be necessary to strengthen readiness for future risks.
The Intersection of Cyber and Third-Party Risk
Increasingly, modern businesses are reliant on their extended network for mission-critical products and services. They no longer operate as standalone entities but as an ecosystem comprising of multiple third parties, including contractors, consultants, technology providers, and more.
With the growing digital dependencies among organizations, the risk of security breaches through third parties has also increased manifold. Forrester’s Predictions Blog 2022 indicates that 60% of security incidents can be traced back to third parties.
With the number of third parties often running into hundreds, it is difficult for an organization to monitor them effectively, leading to blind spots and vulnerability to third-party cyber-attacks. In a recent survey sponsored by MetricStream, 76% of IT leaders and influencers rated managing third-party risk as a high or critical priority in their organizations. For the majority of respondents (74%), this priority has increased since 2020, when the pandemic caused significant micro and macro disruptions, including supply and workforce shortages.
The situation is further exacerbated due to digital interconnectedness. A security incident at one organization can quickly spread and paralyze several other interconnected businesses. Recent incidents highlight the increasingly precarious digital environment businesses navigate. As the complexity of business systems increases and digital dependencies between third-party players continue to evolve, this figure will only continue to rise.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve continuously, organizations need to stay on top of their attack surface and extended enterprise. They need to proactively identify the critical third parties as well as fourth and nth parties and take the right steps – due diligence, monitoring, onsite and offsite risk and compliance assessments, etc. – to effectively mitigate the associated risks.
A connected approach to managing interconnected risks assumes even greater significance in a threat environment that is not simply interconnected but in a constant state of flux.
How MetricStream Helped Mastercard Build a Safer Payments Ecosystem with a Fourth-Party Risk Monitoring Program
Being one of the world’s largest payments technology providers, Mastercard has a highly complex operational ecosystem comprising of several third-and fourth-party vendors. Previously, the company had no visibility into the risk controls in place for fourth parties brought by customers to its ecosystem. To overcome this challenge, the payments giant took a proactive step of building a new fourth-party risk management program from the ground up. It chose MetricStream Third-Party Risk Management, built on the MetricStream Platform and running on the AWS cloud.
With the implementation, Mastercard now has a unified, holistic view of all third- and fourth-party risks and can perform faster risk assessments with automatic segmentation of fourth parties into various risk categories. The efficiency of assessment processes has significantly improved with the automatic distribution of questionnaires and population of responses. The solution also provides actionable and timely fourth-party risk insights, thereby accelerating Mastercard’s risk response.
5 Recommendations to Tackle Interconnected Risks
To effectively tackle interconnected risks, organizations need a connected approach to GRC, enabling them to look at the big picture, identify existing and emerging risks, and understand risk relationships and impact. Here are our top 5 recommendations for organizations to efficiently manage interconnected risks:
#1 Risk Quantification
Risk quantification, or expressing risk exposure in monetary terms, is critical for organizations to accurately understand their risk exposure in the context of their risk appetite, determine which risks to focus on first, and ensure optimum utilization of resources. PwC’s 2021 Digital Trust Insights Survey found that 60% of cyber managers are starting to quantify cyber risks, with a further 17% formulating plans to start soon.
Moreover, quantifiable metrics allow CROs and CISOs to communicate the organizational risk posture to the board and management in an actionable manner. By improving their understanding of organizational risk exposure, they are better equipped to optimize their risk management efforts – and determine whether to accept, reject, mitigate, or transfer risk.
#2 Control Harmonization
Organizations today need to operate within regulatory parameters and ensure compliance or face regulatory action. Not adhering to various regulations and standards can also undermine a company’s credibility. To ensure compliance with multiple regulations, organizations must set up hundreds of controls. Relying on a manual and siloed approach is not only time and resource-intensive but also leads to the duplication of controls.
Control harmonization is a process that standardizes control sets to help you comply with multiple regulations and standards simultaneously. Organizations can significantly improve their compliance management processes and save time, effort, and costs by mapping controls to regulations, standards, policies, risks, processes, and assets
#3 Automation and Analytics
In a constantly evolving risk environment, agility and efficiency are crucial. The traditional GRC approach relies on manual efforts, spreadsheets, and point solutions, and cannot meet the demands of various departments – risk, compliance, audit, cybersecurity, and others. Leveraging advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, etc., can support GRC professionals by improving risk visibility and foresight and making timely and well-informed business decisions.
AI can be a game-changer as it can assist businesses in gaining insights quickly, helping them recognize patterns, avoid duplication of effort, apply appropriate actions, and drive risk-aware decision-making.
#4 Continuous Monitoring
A highly digitized and agile workplace calls for real-time risk insights. Monitoring risk, regulations, and controls is no longer a one-time occurrence but a continuous, real-time activity.
Continuous monitoring – particularly when it comes to the effectiveness of controls -- is an essential element of a forward-looking GRC program. It enables preemptive notification of potential risks and control gaps/weaknesses enabling GRC professionals to remediate and resolve issues faster, enhancing compliance and strengthening business resilience.
#5 Collaboration and Communication
Communication and collaboration are the very foundations of managing the interconnectedness of risks. It is essential to drive communication and collaboration across business units and teams, from the board and senior management to the front line, to guarantee the effective implementation of a connected GRC strategy. Only then can an organization eliminate silos and make risk-aware business decisions. Communication is also essential to help businesses quickly switch to crisis-response mode, guided by a playbook designed through collaboration and efficiently shared.
Because the front line is closely involved in day-to-day operations, they are more likely to recognize emerging risks, gaps, and observations that may pose a serious risk to the organization. Empowering them with intuitive and easy-to-use tools to report any observation or anomaly can go a long way in strengthening the overall risk posture.
How MetricStream Can Help
ConnectedGRC
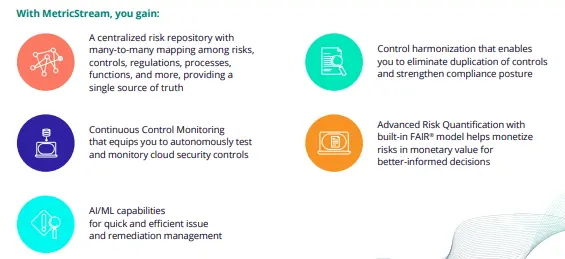
MetricStream ConnectedGRC helps you take an integrated and holistic approach to GRC and ensures collaboration between risk, compliance, audit, cybersecurity, and sustainability teams. Designed with advanced analytics and AI capabilities at the core, it enables businesses to proactively identify, assess, manage, and mitigate various risks.
CyberGRC
MetricStream CyberGRC enables enterprises to actively manage cyber risk and compliance requirements through a comprehensive IT and cyber risk and compliance framework aligned with recognized security standards. It improves visibility into the overall cyber GRC posture and helps you determine cybersecurity investment priorities.
Learn more about MetricStream’s CyberGRC capabilities
Enterprise risk management is becoming an increasingly complex business function. Today, organizations must tackle multiple risks – cyber, geopolitical, third-party, physical, privacy, financial, ESG, and many more. With the larger business environment becoming increasingly digitized and interconnected with ongoing digital transformations, expansion of the internet, cloud adoption, and mobile computing, these diverse risk categories are constantly evolving and becoming more intertwined.
Organizations across industries need to develop a deeper understanding of all the risks they face and their interrelationships. The pandemic further underscored our interconnectedness. It has demonstrated that the volume and velocity of risks and intersection points would only increase going forward.
With the interconnectedness of risks continuing to intensify, organizations must adopt an integrated and holistic approach to risk management and the overarching governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) management framework. GRC professionals can no longer analyze risks in isolation – they need to understand their cascading impacts and devise business resilience strategies effectively.
This eBook will delve into the interconnectedness of risks, closely examine the intersection of third-party and cyber risks, and discuss key strategies for organizations to tackle complex risk relationships effectively.
Risks do not exist in isolation. There are always multiple points of intersection. Consider, for example, geopolitical risk. As a result of the continuous power conflicts among global powers, there will inevitably be supply chain disruptions, increased danger of state-sponsored cyber attacks, changes in government regulations and policies, and more. At the same time, cyber-attacks lead to operational, financial, reputational, and other risks, and so on. This interconnectedness of risks results in a complex web of risk relationships.

If these risks are not viewed from a macro-perspective, they will continue to evolve within their silos, eventually culminating in a systemic, industry-wide collapse.
Risk managers must assess the organizational risk posture by analyzing the impact of risk on all interrelated categories, including operational, strategic, systemic, regulatory, technology, security, third-party, and physical risks. A disruption anywhere along the transaction chain can cause ripples across the market. A failure to comprehend and assess interdependencies can lead to shortsighted decisions and hamper recovery efforts.
The traditional approach to risk management – relying on siloed processes, manual effort, and spreadsheets – falls short of providing comprehensive visibility into risks and risk relationships. A GRC strategy designed for the future must have an integrated and connected approach at its core. It should not only provide visibility into risk interconnectedness but also how risks are tied to assets, controls, regulations, processes, etc., for a true understanding of the overall GRC posture. Combined with automated and autonomous workflows, this forward-looking and resilience-focused GRC approach will be necessary to strengthen readiness for future risks.
Increasingly, modern businesses are reliant on their extended network for mission-critical products and services. They no longer operate as standalone entities but as an ecosystem comprising of multiple third parties, including contractors, consultants, technology providers, and more.
With the growing digital dependencies among organizations, the risk of security breaches through third parties has also increased manifold. Forrester’s Predictions Blog 2022 indicates that 60% of security incidents can be traced back to third parties.
With the number of third parties often running into hundreds, it is difficult for an organization to monitor them effectively, leading to blind spots and vulnerability to third-party cyber-attacks. In a recent survey sponsored by MetricStream, 76% of IT leaders and influencers rated managing third-party risk as a high or critical priority in their organizations. For the majority of respondents (74%), this priority has increased since 2020, when the pandemic caused significant micro and macro disruptions, including supply and workforce shortages.
The situation is further exacerbated due to digital interconnectedness. A security incident at one organization can quickly spread and paralyze several other interconnected businesses. Recent incidents highlight the increasingly precarious digital environment businesses navigate. As the complexity of business systems increases and digital dependencies between third-party players continue to evolve, this figure will only continue to rise.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve continuously, organizations need to stay on top of their attack surface and extended enterprise. They need to proactively identify the critical third parties as well as fourth and nth parties and take the right steps – due diligence, monitoring, onsite and offsite risk and compliance assessments, etc. – to effectively mitigate the associated risks.
A connected approach to managing interconnected risks assumes even greater significance in a threat environment that is not simply interconnected but in a constant state of flux.
How MetricStream Helped Mastercard Build a Safer Payments Ecosystem with a Fourth-Party Risk Monitoring Program
Being one of the world’s largest payments technology providers, Mastercard has a highly complex operational ecosystem comprising of several third-and fourth-party vendors. Previously, the company had no visibility into the risk controls in place for fourth parties brought by customers to its ecosystem. To overcome this challenge, the payments giant took a proactive step of building a new fourth-party risk management program from the ground up. It chose MetricStream Third-Party Risk Management, built on the MetricStream Platform and running on the AWS cloud.
With the implementation, Mastercard now has a unified, holistic view of all third- and fourth-party risks and can perform faster risk assessments with automatic segmentation of fourth parties into various risk categories. The efficiency of assessment processes has significantly improved with the automatic distribution of questionnaires and population of responses. The solution also provides actionable and timely fourth-party risk insights, thereby accelerating Mastercard’s risk response.
To effectively tackle interconnected risks, organizations need a connected approach to GRC, enabling them to look at the big picture, identify existing and emerging risks, and understand risk relationships and impact. Here are our top 5 recommendations for organizations to efficiently manage interconnected risks:
#1 Risk Quantification
Risk quantification, or expressing risk exposure in monetary terms, is critical for organizations to accurately understand their risk exposure in the context of their risk appetite, determine which risks to focus on first, and ensure optimum utilization of resources. PwC’s 2021 Digital Trust Insights Survey found that 60% of cyber managers are starting to quantify cyber risks, with a further 17% formulating plans to start soon.
Moreover, quantifiable metrics allow CROs and CISOs to communicate the organizational risk posture to the board and management in an actionable manner. By improving their understanding of organizational risk exposure, they are better equipped to optimize their risk management efforts – and determine whether to accept, reject, mitigate, or transfer risk.
#2 Control Harmonization
Organizations today need to operate within regulatory parameters and ensure compliance or face regulatory action. Not adhering to various regulations and standards can also undermine a company’s credibility. To ensure compliance with multiple regulations, organizations must set up hundreds of controls. Relying on a manual and siloed approach is not only time and resource-intensive but also leads to the duplication of controls.
Control harmonization is a process that standardizes control sets to help you comply with multiple regulations and standards simultaneously. Organizations can significantly improve their compliance management processes and save time, effort, and costs by mapping controls to regulations, standards, policies, risks, processes, and assets
#3 Automation and Analytics
In a constantly evolving risk environment, agility and efficiency are crucial. The traditional GRC approach relies on manual efforts, spreadsheets, and point solutions, and cannot meet the demands of various departments – risk, compliance, audit, cybersecurity, and others. Leveraging advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, etc., can support GRC professionals by improving risk visibility and foresight and making timely and well-informed business decisions.
AI can be a game-changer as it can assist businesses in gaining insights quickly, helping them recognize patterns, avoid duplication of effort, apply appropriate actions, and drive risk-aware decision-making.
#4 Continuous Monitoring
A highly digitized and agile workplace calls for real-time risk insights. Monitoring risk, regulations, and controls is no longer a one-time occurrence but a continuous, real-time activity.
Continuous monitoring – particularly when it comes to the effectiveness of controls -- is an essential element of a forward-looking GRC program. It enables preemptive notification of potential risks and control gaps/weaknesses enabling GRC professionals to remediate and resolve issues faster, enhancing compliance and strengthening business resilience.
#5 Collaboration and Communication
Communication and collaboration are the very foundations of managing the interconnectedness of risks. It is essential to drive communication and collaboration across business units and teams, from the board and senior management to the front line, to guarantee the effective implementation of a connected GRC strategy. Only then can an organization eliminate silos and make risk-aware business decisions. Communication is also essential to help businesses quickly switch to crisis-response mode, guided by a playbook designed through collaboration and efficiently shared.
Because the front line is closely involved in day-to-day operations, they are more likely to recognize emerging risks, gaps, and observations that may pose a serious risk to the organization. Empowering them with intuitive and easy-to-use tools to report any observation or anomaly can go a long way in strengthening the overall risk posture.
ConnectedGRC
MetricStream ConnectedGRC helps you take an integrated and holistic approach to GRC and ensures collaboration between risk, compliance, audit, cybersecurity, and sustainability teams. Designed with advanced analytics and AI capabilities at the core, it enables businesses to proactively identify, assess, manage, and mitigate various risks.
CyberGRC
MetricStream CyberGRC enables enterprises to actively manage cyber risk and compliance requirements through a comprehensive IT and cyber risk and compliance framework aligned with recognized security standards. It improves visibility into the overall cyber GRC posture and helps you determine cybersecurity investment priorities.

Learn more about MetricStream’s CyberGRC capabilities








